- Anki (Software) shared deck downloads
- Hiragana with stroke diagrams and audio
- Hiragana is the alphabet of Japanese (the other two are not for absolute beginners)
- Regions and prefectures of Japan
- Prefectures in Japan
- ˈprēˌfek(t)SHər/
- a district under the government of a prefect
- video.about.com/japanese/Learn-Japanese--What-Are-Hiragana-Characters-.htm
- [PPT] The Japanese Writing System
- syllabaries
- symbol for every syllable
- called kana
- vowels
- [PPT] Tips for learning Japanese: Research perspectives and ...
- **Intrinsic motivation** - inherent pleasure doing it
- IM-knowledge
- pleasure felt learning new things
- IM-accomplishments
- enjoyment inherent in mastering challenges or grasping a difficult construct
- Identify long-term and short-term goals
- Make overall plan to achieve your short-term and long-term goals
- Choose a task to achieve short terms goals and work on it
- Choose an enjoyable task that is slightly difficult but not too difficult, such as reading books, watching anime or drama, listening to J-pop, playing games, etc. (IM-knowledge & IM-esthetics, IM-accomplishment)
- Regularly check and reflect on what has worked or not worked, using checklists and logs.
- If your original goals are found to be a bit unrealistic, modify your goals and plans to make them more realistic.
- Relax and pay attention to the sign of stress.
- Reward yourself when you have done well on a L2 task.
- Do not compare yourself with others.
- IM-stimulation
- general aesthetic pleasure of the experience
- e.g., the high that I experience while speaking
- External motivation
- Integrated regulation
- supports a valuable component of one’s identity and self-concept
- Identified regulation
- learning will help achieve an important personal goal
- Introjected regulation
- Imposing pressure to perform an activity
- e.g., I feel guilty if I didn’t know the language
- External regulation
- complete external control over the activity by the expectation of rewards or punishments
- e.g. to get a job
- Amotivation
- absence of motivation
- e.g., I don’t really understand what I am doing
- Learning Strategies
- techniques to support autonomous long-term learning
- Memory Strategies
- Creating mental linkages, applying images and sounds, reviewing well, employing action
- Cognitive Strategies
- Practicing, receiving and sending messages, analyzing and reasoning, creating structure for input and output
- Compensation Strategies
- Guessing intelligently, overcoming limitations in speaking and writing
- Speakingrisk-taking, paraphrasing, circumlocution, self-monitoring, self-evaluationListeningelaborating, inferencing, selective attention, self-monitoringReadingwhispered reading, guessing, deduction, summarizingWriting:planning, self-monitoring, deduction, substitution
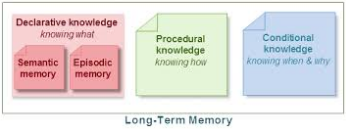
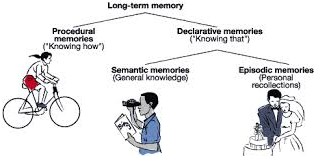
- Most classroom learners are taught declarative knowledge (knowing “that”). Key to successful language learning is how fast you can move from the declarative knowledge stage to the procedural knowledge stage (knowing “how”).
- Doing; cannot be easily explained verbally, and cannot obtained without a lot of practice in using language
- processed unconsciously and automatically~extremely fast language processing
- Grammar
- Grammar explanation helps to acquire the declarative knowledge, but it does not convert into the procedural knowledge without practice.
- Mechanical drills such as repetitions help improve pronunciation, but no correlation is found between the amount of participation in mechanical drills and grammatical acquisition.
- Repetition for confirmation/clarification checks are more effective in internalizing grammar.
- Learn a lot of expressions that help you to negotiate meanings and use them during conversation (Long, 1991)
- Comprehension check (e.g.(私がいったことが/いみが) わかりますか?(この表現は/意味は)正しいですか。まちがっていませんか。)
- Confirmation check (e.g., 〜ですね。〜っていうことですか?〜っていいましたか, 〜ですか)
- Repetition Clarification request (e.g, あのう、今よくわからなかったんですけど, 〜がわからなかったんですけど, もういちどいってくれませんか, 〜ってなんですか。
- (See chat sites below.) After speaking
- Try to write down what you have talked about and check the forms on your own.
- Use check list (noticing log to find out what you have been able to or not able to do during the conversation.
- [Where I left off:] Word knowledge (Mental lexicon) (Levelt, 1993)
- Speak in a Week email course
- Info about learning a language
- One-on-one conversation sites
- keyboard
Monday, November 17, 2014
My beginning
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)


No comments:
Post a Comment